Understanding Target Stock Price Graphs
Target stock price graphs are visual representations of a stock’s price movements over time. Understanding how to read and interpret these graphs is crucial for making informed investment decisions. This section will break down the key components, types, and interpretations of these graphs.
Components of a Target Stock Price Graph
A typical target stock price graph displays several key components: the x-axis representing time (usually days, weeks, or months), the y-axis representing the stock’s price, and the plotted data points showing the price at specific time intervals. Additional elements often include volume indicators, moving averages, and technical indicators (discussed later).
Types of Target Stock Price Graphs
Several types of graphs are used to represent stock prices. Line graphs provide a simple, continuous view of price changes over time. Bar graphs show price changes over specific periods, such as daily highs and lows. Candlestick charts combine price range information (high, low, open, close) into a single visual element, offering a more detailed representation of price movements and market sentiment.
Relationship Between Time, Price, and Volume
The relationship between time, price, and volume is fundamental to understanding stock price trends. Price changes over time indicate the stock’s performance. Volume indicates the trading activity; high volume often accompanies significant price movements, suggesting strong market interest. Low volume price movements may indicate less conviction behind the price change.
Sample Stock Price Data
Source: dreamstime.com
| Date | Open Price | High Price | Low Price | Close Price | Volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023-01-01 | 100 | 102 | 98 | 101 | 100000 |
| 2023-02-01 | 101 | 105 | 100 | 104 | 150000 |
| 2023-03-01 | 104 | 106 | 102 | 105 | 120000 |
| 2023-04-01 | 105 | 108 | 103 | 107 | 180000 |
Interpreting Price Trends
Identifying trends is key to using stock price graphs effectively. This section details how to identify trends, the significance of support and resistance levels, and the role of moving averages.
Key Indicators of Upward and Downward Price Trends
Upward trends are characterized by progressively higher highs and higher lows. Downward trends show progressively lower highs and lower lows. Sideways or “consolidating” trends exhibit price fluctuations within a defined range.
Support and Resistance Levels
Support levels represent price points where buying pressure is expected to outweigh selling pressure, preventing further price declines. Resistance levels are price points where selling pressure is anticipated to exceed buying pressure, halting upward price movements. These levels are often identified by observing previous price reversals.
The Role of Moving Averages
Moving averages smooth out price fluctuations, revealing underlying trends. Commonly used moving averages include the 50-day and 200-day moving averages. A price crossing above a moving average often suggests a bullish signal, while a cross below suggests bearish sentiment.
Visual Representation of an Upward Trend
Imagine a graph where the price line steadily increases over time. A horizontal line representing the support level is situated below the price line, while another horizontal line representing the resistance level is above, but the price line never breaches it. A slightly sloped line, representing the 50-day moving average, runs parallel to and below the price line, confirming the upward trend.
Factors Influencing Target Stock Prices: Target Stock Price Graph
Numerous factors influence stock prices. This section explores macroeconomic influences, company-specific news, and other potential causes of price fluctuations.
Macroeconomic Factors
Interest rate changes, inflation rates, economic growth, and geopolitical events all significantly impact stock prices. For instance, rising interest rates can decrease stock valuations as investors seek higher returns from bonds. Recessions can lead to widespread stock price declines.
Company-Specific News
Positive news, such as strong earnings reports, new product launches, or strategic partnerships, typically boosts stock prices. Conversely, negative news, including profit warnings, product recalls, or legal issues, often leads to price drops. The magnitude of the impact depends on the news’s significance and the market’s reaction.
Effects of Positive and Negative News
Positive news is usually reflected in a sharp upward movement in the stock price graph, often accompanied by increased trading volume. Negative news typically causes a downward price movement, potentially with high volume depending on the severity of the news.
Potential Factors Causing Significant Price Fluctuations
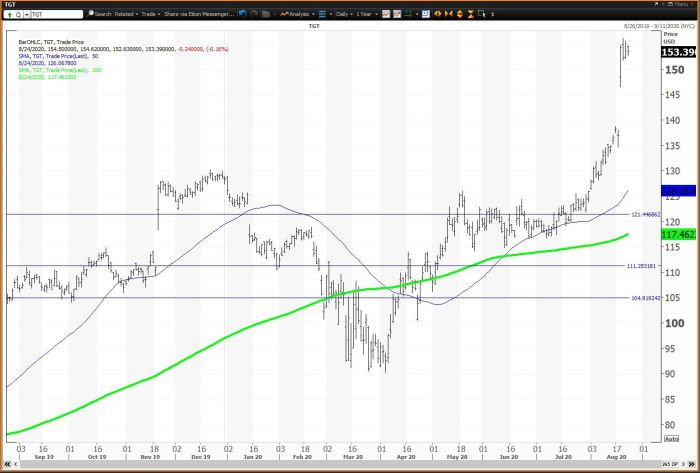
Source: investopedia.com
- Major economic shifts: Recessions or booms drastically affect investor sentiment and stock valuations.
- Regulatory changes: New regulations can impact a company’s operations and profitability, leading to price swings.
- Technological advancements: Disruptive technologies can create opportunities or threats, influencing stock prices.
- Geopolitical instability: Wars, trade disputes, or political uncertainty create market volatility.
- Unexpected events: Natural disasters, pandemics, or other unforeseen events can cause significant price fluctuations.
Using Target Stock Price Graphs for Investment Decisions
Target stock price graphs are valuable tools for identifying potential investment opportunities. This section explores how to use them to make informed decisions, considering risk and reward.
Identifying Buying or Selling Opportunities
Buying opportunities might be identified when the price reaches a support level, showing potential for a rebound, or when a clear upward trend is established. Selling opportunities could arise when the price hits resistance, suggesting potential for a pullback, or during a confirmed downward trend.
Risk and Reward
Risk and reward are intrinsically linked to stock investing. Higher potential rewards often come with higher risk. Analyzing price graphs helps assess the potential risk by identifying support and resistance levels and understanding the volatility of the stock. Reward is assessed by the potential price appreciation.
Hypothetical Investment Scenario
Source: amazonaws.com
Imagine a stock trading near its support level after a period of decline. Technical indicators suggest a potential bottom, and the 50-day moving average is turning upward. This combination could indicate a potential buying opportunity, as the risk of further price decline is reduced while the potential for price appreciation is increased.
Step-by-Step Process for Evaluating a Stock’s Potential
- Analyze the long-term trend: Is the stock in an upward, downward, or sideways trend?
- Identify support and resistance levels: Where are the key price levels that have historically held?
- Observe volume: Does the volume confirm price movements?
- Examine moving averages: What do the moving averages suggest about the trend?
- Consider technical indicators: Do indicators like RSI or MACD provide additional insights?
- Assess overall market conditions: How does the stock’s performance relate to the broader market?
Advanced Graph Analysis Techniques
More advanced techniques can enhance the interpretation of stock price graphs. This section explores the use of technical indicators and chart patterns.
Application of Technical Indicators
Technical indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) provide insights into momentum and potential overbought or oversold conditions. RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. MACD uses moving averages to identify changes in momentum.
Use of Chart Patterns
Chart patterns, such as head and shoulders, double tops, and double bottoms, can predict potential price reversals. A head and shoulders pattern, for instance, often signals a potential price decline.
Comparison of Analysis Methods
Different methods, including fundamental analysis (evaluating a company’s financial health) and technical analysis (using price charts and indicators), offer different perspectives. A comprehensive approach often combines both.
Limitations of Using Target Stock Price Graphs Alone
Stock price graphs are valuable tools but shouldn’t be the sole basis for investment decisions. External factors, unforeseen events, and qualitative factors not reflected in the graph can significantly impact stock prices. Thorough research, including fundamental analysis, is essential.
FAQ Insights
What are the limitations of relying solely on target stock price graphs for investment decisions?
Stock price graphs reflect past performance, not future guarantees. External factors (economic shifts, unforeseen events) can significantly impact prices, rendering even the most sophisticated analysis inaccurate. Fundamental analysis and diversification are essential complements.
How frequently should I review a target stock price graph?
Frequency depends on your investment strategy and risk tolerance. Active traders might check daily, while long-term investors may review weekly or monthly. Regular monitoring allows for timely adjustments based on emerging trends.
Understanding a target stock price graph requires careful analysis of various market factors. A key aspect of this analysis often involves comparing the target with the performance of similar companies; for instance, checking the current trajectory, as seen on the stock price wmb graph, can provide valuable context. Returning to the target stock price graph, this comparative data helps refine predictions and assess the reasonableness of projected values.
Where can I find reliable, real-time target stock price graphs?
Many reputable financial websites and brokerage platforms offer real-time stock charts. Ensure the source is trustworthy and provides accurate, up-to-date data.
